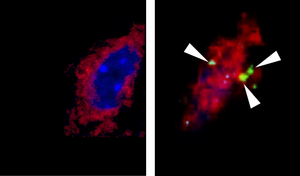
picture: Confocal microscope photos exhibiting, on the left, the presence of the protein IL6 (inexperienced) in ventromedial hypothalamic neurons (pink) in resting mice and, on the correct, in mice after an train session
view extra
Credit score: Eduardo Ropelle/FCA-UNICAMP
An article revealed in Science Advances describes for the primary time a neuromuscular circuit that hyperlinks the burning of muscle fats to the motion of a protein within the mind.
The findings, obtained in Brazil by researchers on the State College of Campinas (UNICAMP) and the College of São Paulo (USP), contribute to a deeper understanding of how common bodily train helps weight reduction, reinforcing the significance of this behavior to good well being.
“We got down to examine the motion of a protein referred to as interleukin 6 [IL-6], which is a pro-inflammatory cytokine however performs completely different capabilities in some conditions together with train. On this case, the perform is burning muscle fats,” mentioned Eduardo Ropelle, final writer of the article. Ropelle is a professor at UNICAMP’s Faculty of Utilized Sciences (FCA) in Limeira and is supported by FAPESP.
The group led by Ropelle had already noticed in mice that muscle fats oxidation started instantly within the legs when the protein was injected instantly into the mind. This a part of the examine was carried out through the grasp’s analysis of Thayana Micheletti, with a scholarship from FAPESP.
Micheletti carried out a part of the evaluation throughout a analysis internship on the College of Santiago de Compostela in Spain.
The researchers analyzed the outcomes to search out out whether or not there was a neural circuit linking manufacturing of IL-6 within the hypothalamus, a mind area that controls a number of capabilities, to the breakdown of skeletal muscle fats. This a part of the examine was carried out with the collaboration of Carlos Katashima, who’s at present on a postdoctoral internship at FCA-UNICAMP’s Laboratory of Molecular Biology of Train (LaBMEx), headed by Ropelle.
Earlier research confirmed {that a} particular a part of the hypothalamus (the ventromedial nucleus) might alter muscle metabolism when stimulated. On detecting the presence of IL-6 receptors on this mind area, Brazilian researchers formulated the speculation that the protein produced there would possibly activate a neuromuscular circuit that favored the burning of skeletal muscle fats.
A number of experiments have been carried out to display the circuit’s existence. In a single, Katashima and colleagues excised a part of the sciatic nerve in one of many legs of every mouse. The sciatic nerve runs from the decrease backbone to the ft.
When IL-6 was injected into the mind, fats was burned as anticipated within the intact legs however not within the leg with the severed nerve. “The experiment confirmed that muscle fats is metabolized solely because of the nervous connection between hypothalamus and muscle,” Katashima mentioned.
Blocked receptors
To learn how the nervous system was linked to the muscle mass, the researchers administered medication that blocked the mice’s alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors, on this case chargeable for receiving nervous alerts for muscle mass to carry out the perform decided by the mind.
Blocking beta-adrenergic receptors had little impact, however muscle fats oxidation stopped or was sharply diminished when alpha-adrenergic receptors have been blocked.
Laptop simulations (in silico evaluation) confirmed hypothalamic IL-6 gene expression to be strongly correlated with two muscle alpha-adrenergic receptor subunits (adrenoreceptors alpha2A and alpha2C). When IL-6 was injected into the brains of mice genetically engineered to not produce these receptors, the outcomes have been validated: leg muscle fats was not metabolized in these mice.
“An necessary discovering of the examine was the affiliation between this neuromuscular circuit and afterburn, which is fats oxidation that happens after train has ceased. This has been thought of secondary, however the truth is, it may possibly final for hours and ought to be thought of vitally necessary to the method of weight reduction,” Ropelle mentioned.
“We confirmed that bodily train not solely produces IL-6 in skeletal muscle, which was already recognized but in addition will increase the quantity of IL-6 within the hypothalamus,” Katashima famous. “It’s probably due to this fact that the results final far longer than the period of the train itself, underlining the significance of train to any intervention towards weight problems.”
The FAPESP additionally supported the examine by way of a Thematic Mission led by Adelino Sanchez Ramos da Silva, a co-author of the article and a professor on the Ribeirão Preto Faculty of Bodily Schooling and Sport (EEFERP-USP).
About São Paulo Analysis Basis (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Analysis Basis (FAPESP) is a public establishment with the mission of supporting scientific analysis in all fields of information by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with greater schooling and analysis establishments within the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is conscious that the easiest analysis can solely be accomplished by working with the very best researchers internationally. Due to this fact, it has established partnerships with funding companies, greater schooling, personal firms, and analysis organizations in different international locations recognized for the standard of their analysis and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to additional develop their worldwide collaboration. You possibly can study extra about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and go to FAPESP information company at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to maintain up to date with the most recent scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps obtain via its many packages, awards and analysis facilities. You may additionally subscribe to FAPESP information company at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe
Article Title
Proof for a neuromuscular circuit involving hypothalamic interleukin-6 within the management of skeletal muscle metabolism
Article Publication Date
29-Jul-2022
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! should not chargeable for the accuracy of reports releases posted to EurekAlert! by contributing establishments or for the usage of any info via the EurekAlert system.