Medical characterization
Three wholesome, reasonably energetic people (Desk 1) carried out three 30 s all-out dash workouts with 2 min of restoration between sprints. Peak energy output within the three sprints was on common 8.87 ± 2 W/kg, akin to 10.3 metabolic equivalents (METs). Whole vitality expenditure was 14.5 ± 6.9 KJ.
Mobile yield, composition, and organic processes in numerous cell populations
The tissue retrieval was 500 ± 150 mg per pattern and a complete of 39,015 cells from pre- and 24,332 cells from post-exercise had been analyzed with a imply learn depend of 19,507,451 and 19,328 882, respectively. To research reproducibility and enhance sequence-depth, cells remoted from the third topic had been sequenced twice.
Cell-type annotation and reproducibility
The six samples from the three topics, along with the 2 re-sequenced samples from the third topic, had been built-in, anchored, and clustered (Fig. 1a). Inter-sample reproducibility close to cell-type composition was assessed by a correlation matrix utilizing inter-sample anchoring scores17. Settlement each between and inside topic was constant, with anchoring scores starting from 0.6 to 0.7 (Fig. 1b). All topics contained cells of all cell sorts detected (Fig. 1c), with comparable proportions between samples (Fig. 1d). Thus, the cell-type annotations and anchoring had been extremely reproducible throughout completely different topics and biopsies. Pattern distribution throughout clusters is present in Supplementary Determine 1. Following Leiden-based clustering and cell-type evaluation, six main cell sorts had been recognized: myogenic cells, endothelial cells, pericyte cells, mesenchymal cells, lymphoid cells, and monocyte cells. Cell-type annotation was primarily based on a mix of marker gene expression in comparison with the CellMatch database, the scCatch pipeline18, and an enrichment take a look at of cell sorts through the use of extremely expressed/marker genes in every cluster relative to the transcriptomic profiles of cell sorts offered by the Human Gene Atlas19,20. All populations, besides the pericyte cluster, had been constantly annotated by ≥2 of the strategies and had been due to this fact thought-about unambiguously annotated with respect to mobile origin. Composition tables for particular person samples could be present in Supplementary Information 1.
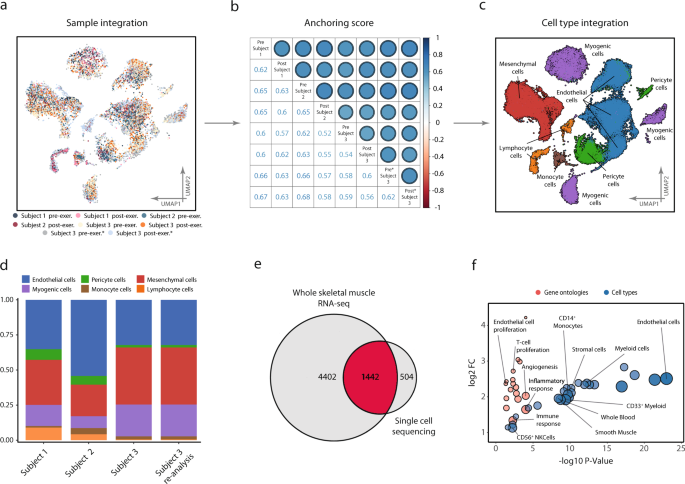
Reproducibility of scRNA-seq between and inside topics. a A complete of 63 000 cells remoted from six vastus lateralis muscle biopsies from three completely different topics had been processed, clustered, and visualized utilizing UMAP projection, with shade coding indicating the contributing donor and pattern. Cells aligned into six main cell populations through which cells from all donors had been evenly distributed, offering a measure of reproducibility of mobile composition. b This was additional confirmed by constant anchoring scores, a measure of correlation between samples, each inside and between topics, as proven within the correlation-matrix. c Cell-type annotation recognized six completely different cell sorts/lineages as indicated on the UMAP. d Cell-type composition in all topics at baseline, together with resequencing of 1 topic to substantiate reproducibility inside and between samples. Endothelial cells had been essentially the most plentiful cell sort constituting 44% of the samples adopted by mesenchymal 26% and myogenic cells at 18%. Full composition could be present in Supplementary Information 1. e Based mostly on the sequencing knowledge from homogenized entire tissue, 5844 transcripts had been recognized as a part of the skeletal muscle transcriptome and 1946 distinctive transcripts had been detected with the scRNA-seq. A considerable proportion (504 or 26%) of those transcripts had been detected solely with the scRNA-seq. f The distinctive transcripts from scRNA-seq evaluation had been extremely enriched in genes from endothelial, immune, and stem cell populations, suggesting that scRNA-seq captures a transcriptional signature of cell populations that in any other case goes largely undetected when utilizing RNA-seq methods.
Comparability with whole-tissue RNA-sequencing
An apparent benefit of scRNA-seq over whole-tissue RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) is the power to deconvolute gene expression profiles into their respective cell-type-based compartments. As well as, it is usually attainable to supply higher protection of gene expression of much less plentiful cell sorts, akin to immune and stem cells. To deal with and objectify this notion, genes detected within the current single-cell experiment had been in contrast with the excellent profile of the skeletal muscle transcriptome out there by means of the Genotype-Tissue Expression knowledge (GTEx)21. Within the 564 skeletal muscle samples from the GTEx research, 5844 distinctive transcripts had been detected readably, whereas within the present single-cell experiment a complete of 1946 distinctive transcripts had been detected. Of the transcripts detected by scRNA-seq, 504 transcripts weren’t readably detected within the GTEx knowledge, representing 26% of all of the transcripts recognized by scRNA-seq (Fig. 1e). Amongst transcripts detected solely within the single-cell experiment, gene and cell ontology evaluation revealed robust enrichment of genes derived from immune, endothelial, mesenchymal, and easy muscle cells (Fig. 1f). Among the many differentially enriched organic processes related to these cell populations had been “constructive regulation of T cell proliferation” (fdr < 0.01), “constructive regulation of angiogenesis” (fdr < 0.01), and “constructive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation” (fdr < 0.05), indicative of cell type-specific enrichments (Fig. 1f).
Mobile composition and cell-type traits
Endothelial cells accounted for 44% of the full variety of cells and had been distributed in 4 distinct however neighboring clusters (ESAM+, VWF+/EPS8+, ACKR1+, and FABP4+/NEAT1−) (Fig. 2a). General, endothelial cells had been characterised by excessive expression of identified endothelial marker genes, together with VWF and ESAM (Fig. 2c, d). As compared with the opposite cell sorts, endothelial cells had a considerably increased expression of 165 genes and enriched for 263 gene ontologies akin to “regulation vasculature improvement” (fdr < 0.05), “actin filament group” (fdr < 0.01), and “response to wounding” (fdr < 0.001) (Fig. 2b). Extra detailed tables of cell-type and subpopulation particular differential expression along with ontology enrichment could be discovered within the Supplemental Info.
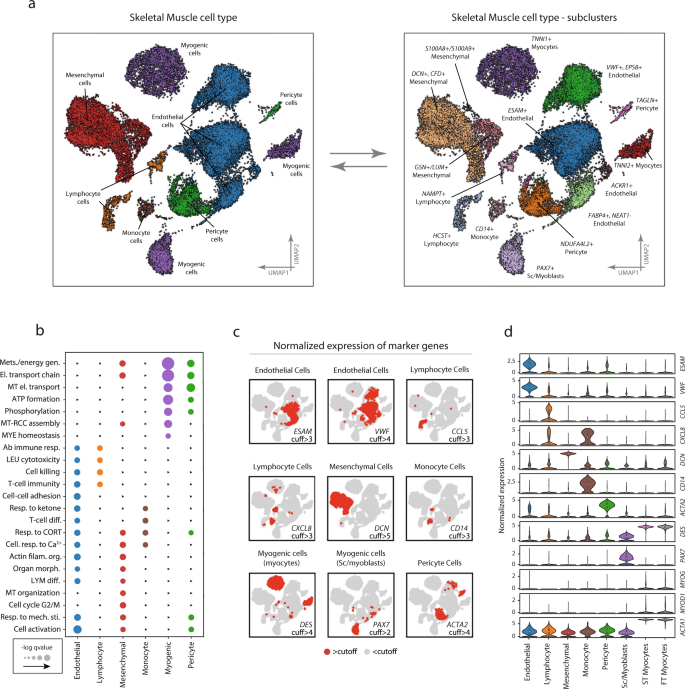
Marker expression, and ontology enrichment throughout the completely different cell sorts and subpopulations. a Cell-type annotation was primarily based on a mix of marker gene expression in contrast with the CellMatch database in relation to profiles of particular cell sorts within the Human Gene Atlas. Six completely different cell sorts/lineages had been recognized and color-coded on the UMAP: Endothelial cells, Myogenic cells, Mesenchymal cells, Myeloid cells, Lymphoid cells, and Pericyte cells. Distinct cell clusters derived from the identical cell sort had been in contrast and characterised by means of differential expression. 4 subpopulations of endothelial cells had been recognized to vary by the expression of VWF+/EPS8+, ESAM+, and FABP4+/NEAT−, respectively. There have been three mesenchymal subpopulations characterised by differential expression of DCN+/CFD+, GSN+/LUM+, and S100A8+/S100A9+, and muscle cells may very well be additional subdivided into three myogenic subpopulations, together with PAX7+ satellite tv for pc/myoblast cells, and fast- (TNNI2+) and slow-twitch (TNNI1+) troponin expressing cells. Pericytes characterised by excessive/marker gene expression of ACTA2 and PDGFR had been divided into two subpopulations (NDUFA4L2+ and TAGLN+). One monocyte inhabitants was discovered to specific CD14. b Enrichment evaluation of organic features within the completely different cell populations exhibits functionally completely different gene expression profiles for the completely different cell sorts. Colour coding represents completely different cell-type and bigger dot radius denotes extra vital organic operate (fdr < 0.05). c Marker gene expression within the completely different cell populations. Pink and grey colours point out the expression of every marker gene above and under laborious threshold in all cells, respectively. d Quantitative comparability of the expression of the marker genes within the completely different cell sorts. The info in boxplots nested inside violin plots are expressed as median, interquartile vary, minimal and most values. Normalized expression refers to log(1 + x) if not said in any other case. SC satellite tv for pc cells; ST slow-twitch, FT fast-twitch, cuff cutoff. Full marker-gene differential expression could be present in Supplementary Information 2–4.
Mesenchymal cells represented 26% of the full variety of cells and confirmed considerably elevated expression of DCN, CFD, and GSN. These cells had been additional divided into three distinct subpopulations (i.e., DCN+/CFD+, GSN+/LUM+, S100A8+/S100A9+) (Fig. 2a, c, d). The ontologies enriched within the mesenchymal cell inhabitants had been generic in nature, together with “autophagy” (fdr < 0.01), “regulation of anatomical construction morphogenesis” (fdr < 0.01), “oxidative phosphorylation” (fdr < 0.01), “electron transport chain” (fdr < 0.01), and “cell activation” (fdr < 0.05) (Fig. 2b). The S100A8+/S100A9+ subpopulation was thought-about ambiguously annotated. Nevertheless, as a result of excessive expression of DCN, VIM, COL6A3, and GSN marker genes the cluster was deemed to be of mesenchymal origin.
Myogenic cells represented 18% of complete cells and had been additional divided into three distinct subpopulations (i.e., PAX7+, TNNI1+, TNNI2+) (Fig. 2a). Along with PAX7, the primary cluster expressed MYF5 and in a smaller frequency MYOD1, indicating this cluster is a mixture of undifferentiated satellite tv for pc cells and early myoblasts. The remaining myogenic subpopulations expressed genes related to extra mature traits akin to DES, MYL2, and MYOG (Fig. 2c, d), and maybe terminally differentiated muscle fibers together with ACTA1 and MYH6. A subset of those cells additionally expressed MYOD1. These two subpopulations had been distinguished from one another by the expression of slow-twitch (TNNI1) and fast-twitch (TNNI2) troponins. On the ontology stage, the myogenic subpopulations exhibited a gene expression profile dominated by key skeletal muscle features akin to “oxidative phosphorylation” (fdr < 0.001) and “mitochondrial respiratory chain” (fdr < 0.001) (Fig. 2b). In line with muscle-specific gene expression, the TNNI1 + and TNNI2 + cells additionally confirmed enrichment for packages concerned in skeletal muscle protein synthesis and degradation (e.g., TRIM63, SYNPO2).
Pericytes accounted for six% of the full cells, with two distinct clusters (TAGLN+ and NDUFA4L2+) (Fig. 2a). The TAGLN+ cluster was characterised by the excessive expression of easy muscle markers akin to ACTA2 and pericyte markers (e.g., PDGFR). As well as, this cluster was additionally annotated as pericyte in origin by scCatch, and due to this fact pericyte was thought-about essentially the most possible mobile origin. Considerably enriched ontologies included “mitochondrial electron transport cytochrome c to oxygen” (fdr < 0.001), “nucleoside triphosphate metabolic course of” (fdr < 0.001), and “oxidative phosphorylation” (fdr < 0.001) (Fig. 2b).
Two lymphocyte clusters (NAMPT+ and HCST+) had been additionally recognized, which accounted for 4% of the full variety of cells (Fig. 2a). Contemplating these clusters introduced gene expression profiles characterizing T-, B-, and NK-cells, they had been collectively thought-about as lymphocytes. Genes that distinguished these clusters from the opposite cell sorts included CCL5 which is taken into account as lymphocyte-specific markers (Fig. 2c, d). Ontological enrichment confirmed “T-cell immunity” (fdr < 0.01), “cell killing” (fdr < 0.05), and “adaptive immune response” (fdr < 0.05).
One monocyte cluster, which accounted for two% of the full variety of cells, was categorised as myeloid in origin, primarily based on CD14 expression (Fig. 2a). The cluster differentially expressed genes together with CXCL8, AIF, and TYROBP (Fig. 2c, d). HLA-DRA was additionally extremely expressed on this cluster, which is a gene related to antigen-presenting cells, attributable to its structural involvement within the formation of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II proteins. These CD14+ monocytes enriched for ontologies together with “multi organism metabolic course of” (fdr < 0.001), “response to corticosterone” (fdr < 0.05), “mobile response to calcium ion” (fdr < 0.05), “response to mineralocorticoid” (fdr < 0.05), “translation initiation” (fdr < 0.001), “Ribosome meeting” (fdr < 0.001), and “Nuclear transcribed mRNA catabolic course of nonsense-mediated decay” (fdr < 0.001) (Fig. 2b). Gene-ontology enrichment and marker gene expression for all cell-types could be present in Supplementary Information 2, 3 and 4 and in Supplementary Fig. 2.
Results of train on mobile composition
The results of excessive depth train had been first examined with respect to mobile composition in skeletal muscle (Fig. 3a). Three hours after train, circulating cells elevated considerably, with lymphocytes rising from 4 to 9% (p = 0.05) and monocytes from 2 to 4% (p < 0.05), with a corresponding lower within the relative contribution of resident cells, i.e., endothelial cells decreased from 44 to 37% and pericytes decreased from 6 to five% after train. The proportion of myogenic cells (18%) remained unchanged after train.
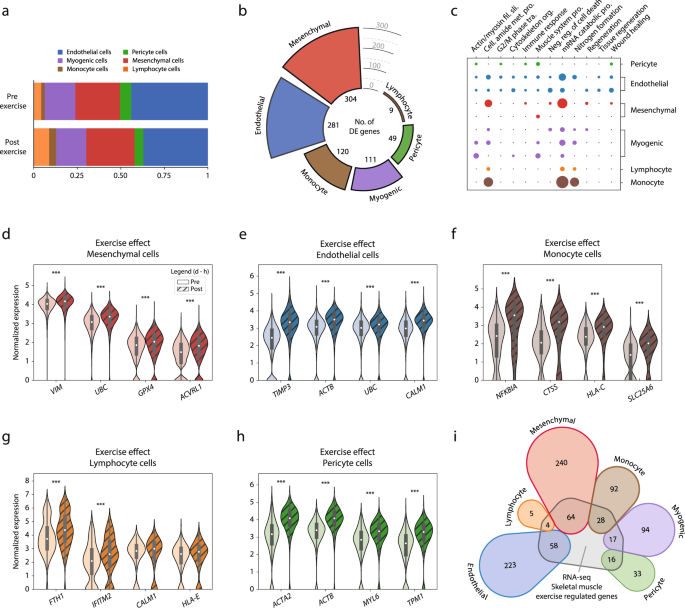
Train results detected by scRNA-seq evaluation of the human skeletal muscle. a Mobile composition evaluation of samples earlier than (pre-exercise) and three hours after (post-exercise) a single bout of train. b Differential expression evaluation throughout cell sorts after a single bout of train. Colour coding represents cell-type, and bar top denotes the variety of exercise-regulated genes. In complete, 874 (535 distinctive) genes had been upregulated by train, with mesenchymal cells having the best quantity (304), adopted by endothelial cells (281) and monocytes (120). In distinction, solely 9 genes had been discovered to reply to the train stimulus within the lymphocyte inhabitants. c Gene-ontology evaluation revealed that the majority organic processes regulated by train had been cell-type particular, with a small variety of processes equally regulated in most cell sorts (“mRNA catabolic course of” and “nitrogen formation”). Colour coding represents completely different cell-type, and a bigger dot radius denotes a extra vital gene ontology (fdr < 0.05). d–h Normalized expression stage of consultant genes for every cell sort that had been differentially expressed after train. The info in boxplots nested inside violin plots are expressed as median, interquartile vary, minimal and most values. ***fdr < 10e−5. i Genes that had been considerably regulated by train within the present scRNA-seq experiment had been in contrast with differentially expressed genes after train utilizing RNA-seq from entire muscle. Colour coding represents completely different cell-type, and numerical worth denotes the variety of differentially expressed genes shared by each strategies or these solely detected by scRNA-seq. Roughly 25% of the genes detected by scRNA-seq had been additionally recognized utilizing RNA-seq and this was constant throughout all cell sorts. Normalized expression refers to log(1 + x) if not said in any other case. Full exercise-differential expression and ontology evaluation could be present in Supplementary Information 5–9.
Transcriptional response to train
The transcriptional response to train was assessed by evaluating pre- vs. post-exercise for every cell sort individually. A complete of 874 (535 distinctive) genes had been differentially expressed (fdr < 0.05) throughout all completely different cell sorts. By way of variety of differentially expressed genes, the mesenchymal cells confirmed the best exercise-related response, with 304 genes differentially expressed (Fig. 3b). In ontological phrases, the mesenchymal cells enriched for organic features concerned in tissue regeneration and transforming, akin to “regeneration” (fdr < 0.01), “organ regeneration” (fdr < 0.05), and “wound therapeutic” (fdr < 0.05) (Fig. 3c). Genes driving the enrichment for regeneration organic operate within the mesenchymal cells included VIM, UBC, GPX4, and AVCRL1 (Fig. 3d). A number of genes concerned in cytoskeletal reorganization and cell-cycle activation, akin to RHOBTB3, TPM1, and RGCC, had been additionally robustly upregulated after train on this cell sort.
The endothelial cells confirmed the second biggest response to train with a complete of 281 differentially expressed genes (Fig. 3b). The principle ontological characterization included cell activation and stress reactions, akin to “cell cycle G2 M-phase transition” (fdr < 0.05), “vitality reserve metabolic response” (fdr < 0.01), and “tissue regeneration” (fdr < 0.05) (Fig. 3c). Differentially expressed genes akin to TIMP3, ACTB, UBC, and CALM1 (Fig. 3e) point out endothelial re-composition and stress response after train.
The myogenic cell populations differentially expressed 111 genes (fdr < 0.05) after train, together with genes concerned in differentiation alongside myogenic lineage akin to MYOD1, and MYF6 (Fig. 4). Within the undifferentiated PAX7+ cluster gene ontologies associated primarily to mobile stress response, akin to “damaging regulation of cell dying” (fdr < 0.001) and “regulation of development” (fdr < 0.05) (Fig. 3c). The genes driving the stress-related enrichments for the PAX7+ cluster included UBC, HSP90AB1, LMNA, NCL, and SOD2. Muscle-related features, akin to “actin-mediated cell contraction” (fdr < 0.001), and “muscle system course of” (fdr < 0.001), had been enriched within the extra mature clusters (TNNI1+, and TNNI2+) (Fig. 3c) and primarily pushed by gene expression akin to DES, ACTA, MYL2, and MYOZ1.
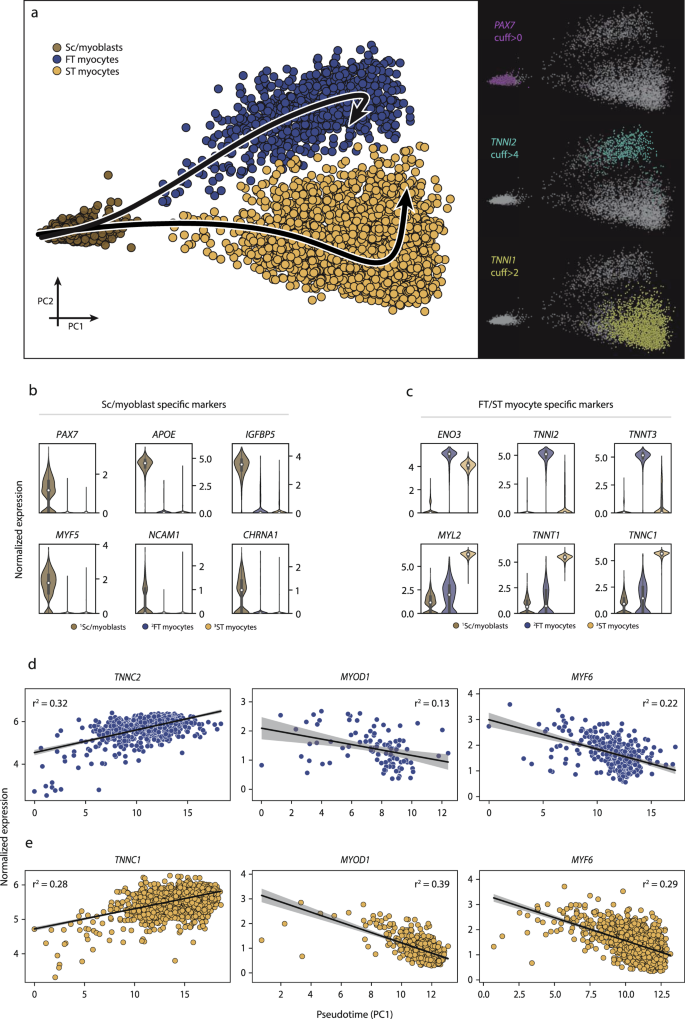
Three distinct myogenic subpopulations of myogenic cells had been recognized and additional investigated for his or her distinguishing options and trajectories. a The primary cluster (brown) was characterised by PAX7+ expression (satellite tv for pc/myoblast cells), whereas the remaining two myogenic subpopulations expressed increased ranges of genes indicative of maturation, together with slow-twitch (TNNI1) and fast-twitch (TNNI2) troponins, alongside their respective trajectories. b, c Extremely expressed genes within the undifferentiated PAX7+ stem/progenitor cell subpopulation relative to the extra differentiated subpopulations. The undifferentiated cell markers included PAX7, NCAM1, MYF5, and APOE, whereas extra differentiated cells expressed ENO3, TNNI1, TNNI2, and MYL2. The info in boxplots nested inside violin plots are expressed as median, interquartile vary, minimal and most values. d, e There was a successive enhance in TNNC1 and TNNC2 expression as cells adopted increased absolute values alongside the trajectory, indicating a steady differentiation course of inside every subpopulation. In parallel, the expression of a number of different genes concerned in differentiation (MYOD1, MYF5) decreased, per the present understanding of the cell maturation alongside the myogenic lineage. Shaded space signifies estimated 95% confidence intervals for the regression estimate. Normalized expression refers to log(1 + x) if not said in any other case. SC satellite tv for pc cells, ST slow-twitch, FT fast-twitch, cuff cutoff.
The monocyte cell inhabitants differentially expressed 120 genes after train (Fig. 3b). Ontologically, the monocytes introduced a generic response to train, with phrases akin to “amide biosynthetic course of” (fdr < 0.001), “protein concentrating on” (fdr < 0.001), and “peptide metabolic course of” (fdr < 0.001) (Fig. 3c). When contemplating the differential expression of single genes, the monocyte inhabitants considerably expressed NFKBIA, CTSS, HLA-C, and SLC25A6 after train, suggesting an inflammatory response and mobile stress reactions to train (Fig. 3f). Lymphocytes differentially expressed 9 genes after train (Fig. 3b). Ontologically, the lymphocyte cells solely enriched for generic phrases, suggesting an absent exercise-specific response. The genes regulating the ontological enrichment had been total generic and lacked established organic features within the literature (e.g., FTH1, IFITM2, CALM1, and HLA-E) (Fig. 3g).
Pericytes differentially expressed 49 genes (Fig. 3b). By way of ontological enrichment, the pericytes confirmed a response indicative of mobile activation, stress response, and regeneration, enriching for 38 ontologies akin to “response to wounding” (fdr < 0.01), “actin mediated cell contraction” (fdr < 0.05), and “cell cycle G2 M part transition” (fdr < 0.05) (Fig. 3c). Genes driving the regenerative response included ACTB, TPM1, TIMP3, and CD36. By way of the best exercise-related response, the pericytes differentially expressed ACTB and ACTA2 after train (Fig. 3h). A whole record of differentially expressed genes and ontologies throughout cell-populations could be present in Supplementary Information 5–8.
Comparability of single-cell with whole-tissue sequencing in relation to train
We additionally examined whether or not the transcriptional responses to train amongst completely different cell populations utilizing scRNA-seq had been per RNA-seq findings. To this finish, the transcriptional responses to train in every cell sort had been in contrast with findings from a current RNA-seq research22 investigating the identical time-points and with the same train protocol as within the present research. Of the 874 transcripts (535 distinctive) that had been considerably regulated in ≥1 cell-type within the present scRNA-seq experiment, 187 transcripts (129 distinctive) had been additionally regulated by train in RNA-seq research (Fig. 3i). There have been no variations between cell populations by way of protection by RNA-seq, i.e., all cell sorts shared ~25% of transcripts regulated by train with RNA-seq.
Trajectory evaluation of myogenic cells
A serious benefit of scRNA-seq is the power to make use of the worldwide transcriptome of every cell to categorise populations of cells of frequent origin right into a continuum of only one to 2 dimensions, thereby visualizing and figuring out successive, stepwise modifications in gene expression from cell to cell. This system is sometimes called trajectory evaluation. Trajectory evaluation has confirmed to be a strong software to deconvolute successive transcription-driven mobile processes in developmental biology and stem cell differentiation. Right here, we use trajectory evaluation to check whether or not there’s proof of a steady transition from undifferentiated myogenic cells into more and more mature myogenic cells (Fig. 4a). Three distinct clusters akin to undifferentiated PAX7+ satellite tv for pc/myoblast cells, TNNI2+ fast-twitch, and TNNI1+ slow-twitch myogenic cells had been chosen, and two completely different trajectories with the undifferentiated cluster as a place to begin had been calculated utilizing principal curve pseudotime evaluation. Genetic markers that decided place alongside the primary principal part included PAX7, APOE, IGFBP5, MYF5, and NCAM1 (Fig. 4b), that are canonical myogenic stem/progenitor cell markers. Among the many extra differentiated cells, ENO3, TNNI2, TNNT3, MYL2, TNNT1, and TNNC1 genes (Fig. 4c) drove the partitioning into distinct clusters alongside the second principal part. The transition of undifferentiated PAX7+ satellite tv for pc/myoblast cells in direction of a better diploma of differentiation was proportional to expression ranges of marker genes alongside the given trajectories. Accordingly, the expression of TNNC1 and TNNC2 elevated proportionally to pseudotime, in slow- and fast-twitch myogenic cells, respectively (r2 = 0.28 and r2 = 0.32, Fig. 4d, e). A corresponding lower within the expression of MYOD1 (r2 = −0.39 and r2 = 0.13) and MYF6 (r2 = −0.29 and r2 = −0.22) was noticed alongside the trajectories for each fast- and slow-twitch cells (Fig. 4d, e).
Moreover, we examined the impact of train on the transition from PAX7+ undifferentiated satellite tv for pc/myoblast cells to fast- and slow-twitch expressing cells and the general transcriptional impact of train in these subpopulations. Three hours after a single bout of train, there was a small (Δslow-twitch = 5.4%, p < 0.001; Δfast-twitch = 9.0%, p < 0.001) however statistically vital incremental shift in pseudotime towards a better diploma of differentiation in each the slow- and fast-twitch cell populations (Fig. 5a, b). Other than the consequences on pseudotime, there was a typical transcriptional response to a single bout of train for twenty-four genes in all three myogenic subpopulations. These genes included largely mitochondrial and ribosomal genes. Extra genes had been regulated by train within the undifferentiated PAX7+ (255 genes) and slow-twitch (138 genes) subpopulations, in comparison with the fast-twitch subpopulation (51 genes) (Fig. 5c). Genes regulated by train within the undifferentiated PAX7+ myogenic cells included NEAT1, NNMT, CXXC5, MT2A, and SQSTM1 (Fig. 5d). The slow-twitch TNNI1+ cells responded to train by regulating genes concerned in “muscle organ improvement” (fdr < 0.001) together with MYLPF, ACTA1, MYL2, and MYH7 (Fig. 5d). Within the fast-twitch TNNI2+ cells, the train response included upregulation of modifications in MYBPC1, MYBCP2 (“muscle contraction”, fdr < 0.001), TXNIP, UBC, and OPTN (Fig. 5d). Gene-ontology enrichment within the myogenic cells following train could be present in Supplementary Information 9.
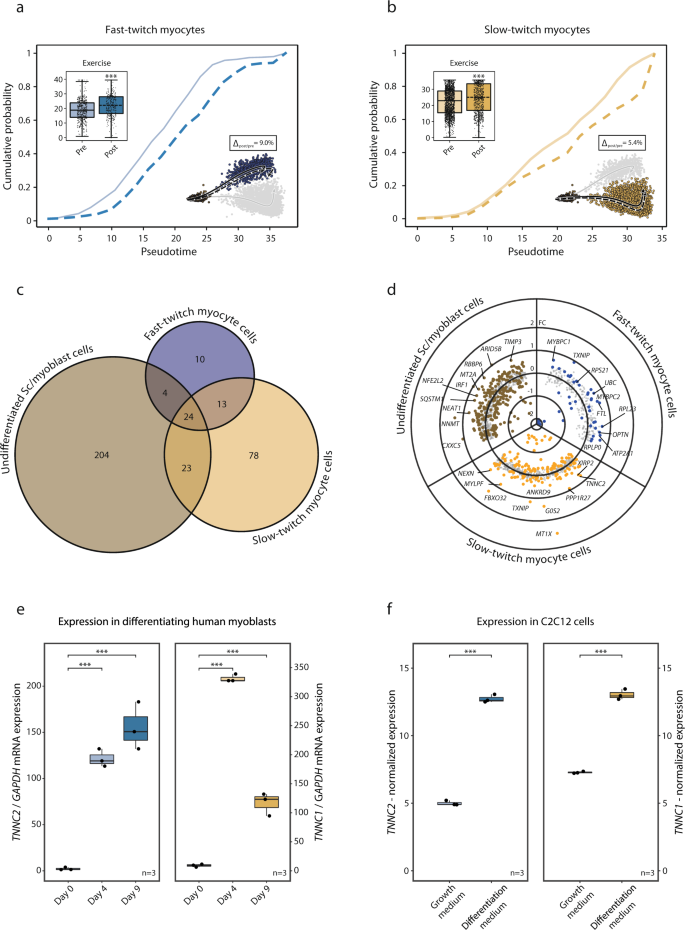
The impact of train on the myogenic cell populations destiny was additional investigated: a, b Three hours post-exercise there was a major change alongside the trajectories with a shift of 9.0 and 5.4% (p < 0.001 for each) in fast- and slow-twitch myogenic cells respectively, indicating elevated differentiation. Boxplots and ECDFs denote the place alongside pseudotime of the myogenic cells pre- vs. post-exercise. c Venn diagram of exercise-regulated genes within the myogenic subpopulations. The bigger train impact was noticed among the many undifferentiated PAX7+ satellite tv for pc/myoblast subpopulation in comparison with the extra mature subpopulations. A considerable portion of the exercise-regulated genes within the extra mature fast- and slow-twitch subpopulations had been additionally regulated within the undifferentiated PAX7+ subpopulation. d Scatter/volcano plot presenting the transcriptional results of train for every myogenic subpopulation. Differentially expressed genes (fdr < 0.05) are highlighted the place distinct shade denotes respective subpopulation. e In vitro validation experiments by means of evaluation of gene expression of slow- and fast-twitch troponins in major human myoblasts present process differentiation. Boxplots depict gene-expression of TNNC2 and TNNC1 mRNA ranges assessed by means of RT-PCR at baseline, after 4 and 9 days of differentiation in direction of myotubes. Statistical evaluation was carried out by means of One-way ANOVA with the Tukey take a look at as a put up hoc. f C2C12 cells in proliferation versus differentiation media with gene expression analyzed utilizing microarrays obtained by means of LIMMA. The place current the information in boxplots are expressed as median, interquartile vary, minimal and most values, and particular person factors are proven as black dots. Normalized expression refers to log2(x) if not said in any other case. SC satellite tv for pc cells.
In vitro validation of myogenic subpopulations
The commentary of a regulated expression of contractile parts akin to TNNC1 and TNNC2 in myogenic cells, and that such transcriptional upregulation is related to the initiation of differentiation in direction of a extra mature myofiber-like phenotype was validated in vitro. Major myoblasts had been remoted from human muscle biopsy and stored in proliferation media till confluence. Differentiation in direction of myotube formation was initiated in keeping with customary protocols and the expression of key-marker genes from the myoblast subpopulations recognized as present process differentiation had been analyzed with qPCR on day 0, day 4, and day 9 of the differentiation course of (Fig. 5e). Gradual-twitch troponin (TNNC1) elevated from 9.3 ± 2 a.u on day 0 to 331 ± 150 after 4 days of differentiation (p < 0.001). It remained elevated after 9 days of differentiation (117 ± 20) (p < 0.001). Gene-expression of fast-twitch troponin (TNNC2) was 2.2 ± 1 a.u on day 0, elevated to 123 ± 10 a.u after 4 days of differentiation (p < 0.001), and remained elevated after 9 days of differentiation (155 ± 30) (p < 0.001).
Lastly, we utilized a publicly out there microarray experiment carried out in a mouse myoblast cell-line (C2C12-cells) analysis gene-expression in cells present process differentiation (n = 3) in relation to cells in proliferation-media (n = 3) (Fig. 5f). TNNC1 and TNNC2 had been elevated with a log2FC of 5.7 and seven.7 respectively (fdr < 0.001) in differentiating versus proliferating C2C12-cells.